Pandit Sethuraman (1925-1997) was an Indian numerologist, astrologer, palmist, and occultist who adopted Cheiro’s alpha-numeric coding of the Latin alphabet and enhanced his system with his own approach. In his youth, he entered military service, during which he began to intensely explore the workings of Chaldean numerology. He claimed that the English alphabet was the correct system for addressing Indian names in modern times. This could be true at least until recently, as post-colonial India was still significantly influenced by the English script. Throughout his life, Pandit Sethuraman also studied astrology, palmistry, yoga, mesmerism, and the energetic system of humans.

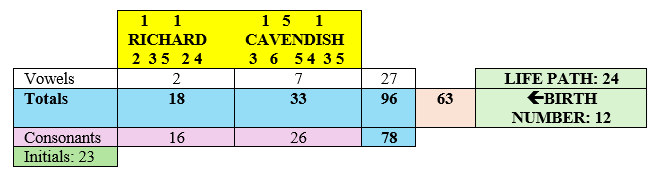
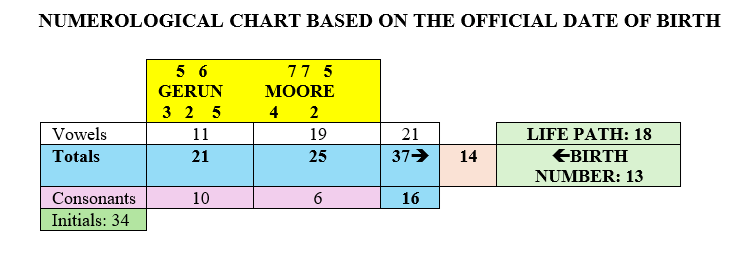
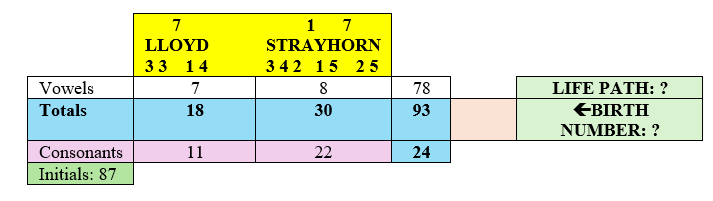
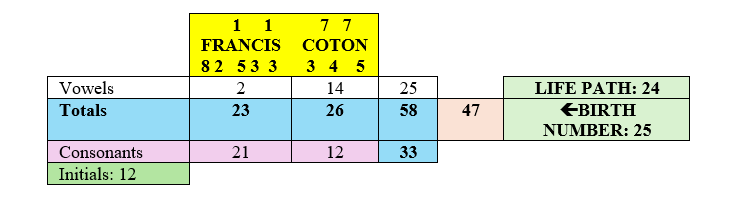
He was born on the 31st of the month, and his Life Path number is 26. The base numbers of these two figures are 4 (3+1=4) and 8 (2+6=8), which are considered karmic numbers. They often bring complications and blows of fate. However, Sethuraman has a strong name numbers 5, particularly in his Total Name Numerology (TNN), which totals 59 (5+9=14; 1+4=5). This active five calms both the 4 and 8 from his birth date numbers and offers some form of escape from karmic limitations.

The main feature of this numerology chart is the relationship between the numbers 5 and 9, or the relationship between Mercury and Mars, which provides good intellect and a certain sense of military. Despite this, Pandit Sethuraman’s numerology chart contains many numbers that are softer or more feminine in nature. Therefore, he was not a typical soldier; he embodied both the energies of clear goals and a sense of softness. Pandit Sethuraman also had “money numbers,” notably involving connections between the numbers 3, 5, and 8. In addition, he had some other indicators pointing in this direction.
The number 9 in his chart was positioned in such a way that it played a very important role in his business and spiritual development. It was associated with 3 and 6, and also with 5. In Sethuraman’s chart it brings an interest in bio-energy, astrology, yoga, and mesmerism. With such numbers, Pandit Sethuraman could have also engaged with Feng Shui or Vastu Shastra. The relationship between the numbers 5 and 9 in this configuration particularly highlights numerology and palmistry as vocational options.
In 1954, he wrote a book titled “Science of Fortune,” in which he revealed some of his insights about numerology. While he adopted Cheiro’s numerological model, he also incorporated Indian traditions, his insights, and messages that he claimed to have received from the Hindu goddess Gayatri.

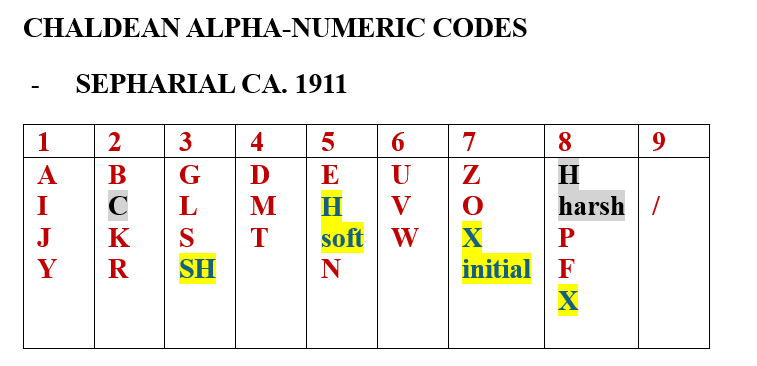
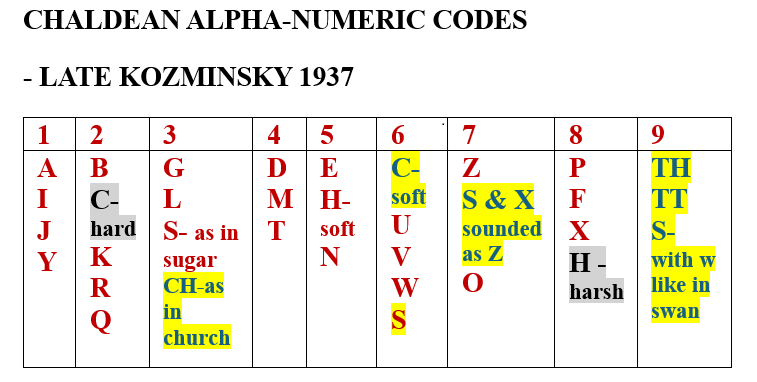
It can be noted that Pandit Sethuraman rejected the complex rules that Cheiro employed to determine the key compound number in someone’s numerology chart. Instead, Pandit Sethuraman simply added the unreduced numbers of the first and last names. When considering the relationships between numbers, a significant influence of the theory of interchangeable numbers is evident. Personally, I use slightly different principles for matching numbers. I can agree with him that, in analyzing partnerships, certain deviations from the general rules of number matching are necessary, although I differ with him on some specific solutions.
His book also contains interesting warnings regarding the use of gemstones to balance someone’s fate and regarding how changing the names and surnames of others can attract unresolved karma from that people. Additionally, Pandit Sethuraman developed his own method for checking the compatibility of a new name and surname with a client’s life energy when intending to change their name.
Using numerology, Pandit Sethuraman predicted the outcomes of military conflicts and the likelihood of someone’s death. He also used numerology for a time when betting on horse races and for financial investments. All of this could quickly lead someone to the edge of ethics, which Pandit Sethuraman was fortunately aware of.
Interestingly, he did not differentiate between strong and weak 8s or between strong and weak 4s; he believed that these two numbers always had the same favorable or unfavorable numbers available. Some rules regarding matching and mismatching between numbers are surprising— for example, he defined the relationship between the numbers 3 and 6 as generally unfavorable.
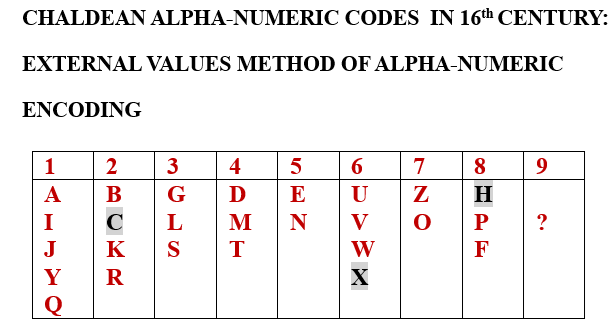
He listed the meanings of the numbers from 1 to 108, claiming that this was the first book on Chaldean numerology that described numbers beyond 52. However, this is not true. Classical Chaldean/Hebrew numerology has even defined some numbers above 108, and in modern numerology, well before Pandit Sethuraman, accepted descriptions of the numbers 55, 65, 69, and 71 can be found. During World War II, one of the Chaldean numerologists adopted the interpretations of numbers presented by the Pythagorean numerologist Mary Adams. Her definitions cover numbers up to and including 65, in addition to the numbers 69, 71, and 73.
Some of Sethuraman’s descriptions of numbers are also questionable— for instance, he defined the number 12 as lucky. Conversely, he classified the numbers 39 and 48 as unlucky forms of the number 12, where he diverged from Cheiro’s descriptions, too. Furthermore, the classical meaning of the number 77 is generally unfavorable, while Pandit Sethuraman defined it as a favorable number.
Regardless, his book offers a wealth of interesting information and provides a researcher of Chaldean numerology with the opportunity for comparative analysis, thus allowing for the search for refined knowledge and new insights.